QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver
$309.00
QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver Module CISCO, HUAWEI, H3C, Juniper, D-link, HP, IBM, dell, Mikrotik, Aruba,Quidway CompatibleThis product is a transceiver module designed for 2m-10km optical communication applications. The design is compliant to 40GBASE-LR4 of the IEEE P802.3ba standard.
What is QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver Module?
QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver Module CISCO, HUAWEI, H3C, Juniper, D-link, HP, IBM, dell, Mikrotik, Aruba,Quidway Compatible This product is a transceiver module designed for 2m-10km optical communication applications. The design is compliant to 40GBASE-LR4 of the IEEE P802.3ba standard. The module converts 4 inputs channels (ch) of 10Gb/s electrical data to 4 CWDM optical signals, and multiplexes them into a single channel for 40Gb/s optical transmission. Reversely, on the receiver side, the module optically de-multiplexes a 40Gb/s input into 4 CWDM channels signals, and converts them to 4 channel output electrical data.The central wavelengths of the 4 CWDM channels are 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nm as members of the CWDM wavelength grid defined in ITU-T G.694.2. It contains a duplex LC connector for the optical interface and a 38-pin connector for the electrical interface. To minimize the optical dispersion in the long-haul system, single-mode fiber (SMF) has to be applied in this module.
Product Features QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver
- Compliant with 40G Ethernet IEEE802.3ba and 40GBASE-LR4 Standard
- QSFP+ MSA compliant
- Compliant with QDR/DDR Infiniband data rates
- Up to 11.2Gb/s data rate per wavelength
- 4 CWDM lanes MUX/DEMUX design
- Up to 10km transmission on single mode fiber (SMF)
- Operating case temperature: 0 to 70℃
- Maximum power consumption 2.5W
- LC duplex connector
- RoHS compliant
Applications QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver
- 40GBASE-LR4 Ethernet Links
- Infiniband QDR and DDR interconnects
- Client-side 40G Telecom connections
Absolute Maximum Ratings It has to be noted that the operation in excess of any individual absolute maximum ratings might cause permanent damage to this module.
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Storage Temperature | TS | -40 | 85 | ℃ | |
| Operating Case Temperature | TOP | 0 | 70 | ℃ | |
| Power Supply Voltage | VCC | -0.5 | 3.6 | V | |
| Relative Humidity (non-condensation) | RH | 0 | 85 | % | |
| Damage Threshold, each Lane | THd | 3.3 | dBm |
Recommended Operating Conditions and Power Supply Requirements
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Typical | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Operating Case Temperature | TOP | 0 | 70 | ℃ | ||
| Power Supply Voltage | VCC | 3.135 | 3.3 | 3.465 | V | |
| Data Rate, each Lane | 10.3125 | Gb/s | ||||
| Control Input Voltage High | 2 | VCC | V | |||
| Control Input Voltage Low | 0 | 0.8 | V | |||
| Link Distance with G.652 | D | 0.002 | 10 | km |
Electrical Characteristics The following electrical characteristics are defined over the Recommended Operating Environment unless otherwise specified.
| Parameter | Test Point | Min | Typical | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Power Consumption | 2.5 | W | ||||
| Supply Current | ICC | 0.7 | A | |||
| Transceiver Power-on Initialization Time | 2000 | ms | 1 | |||
| Transmitter (each Lane) | ||||||
| Single-ended Input Voltage Tolerance (Note 2) | -0.3 | 4.0 | V | Referred to TP1 signal common | ||
| AC Common Mode Input Voltage Tolerance | 15 | mV | RMS | |||
| Differential Input Voltage Swing Threshold | 50 | mVpp | LOSA Threshold | |||
| Differential Input Voltage Swing | Vin,pp | 190 | 700 | mVpp | ||
| Differential Input Impedance | Zin | 90 | 100 | 110 | ohm | |
| Differential Input Return Loss | See IEEE 802.3ba 86A.4.11 | dB | 10MHz- 11.1GHz | |||
| J2 Jitter Tolerance | Jt2 | 0.17 | UI | |||
| J9 Jitter Tolerance | Jt9 | 0.29 | UI | |||
| Data Dependent Pulse Width Shrinkage (DDPWS ) Tolerance | 0.07 | UI | ||||
| Eye Mask Coordinates {X1, X2, Y1, Y2} | 0.11, 0.31 95, 350 | UI mV | Hit Ratio = 5×10-5 | |||
| Receiver (each Lane) | ||||||
| Single-ended Output Voltage | -0.3 | 4.0 | V | Referred to signal common | ||
| AC Common Mode Output Voltage | 7.5 | mV | RMS | |||
| Differential Output Voltage Swing | Vout,pp | 300 | 850 | mVpp | ||
| Differential Output Impedance | Zout | 90 | 100 | 110 | ohm | |
| Termination Mismatch at 1MHz | 5 | % | ||||
| Differential Output Return Loss | See IEEE 802.3ba 86A.4.2.1 | dB | 10MHz- 11.1GHz | |||
| Common Mode Output Return Loss | See IEEE 802.3ba 86A.4.2.2 | dB | 10MHz- 11.1GHz | |||
| Output Transition Time | 28 | Ps | 20% to 80% | |||
| J2 Jitter Output | Jo2 | 0.42 | UI | |||
| J9 Jitter Output | Jo9 | 0.65 | UI | |||
| Eye Mask Coordinates {X1, X2, Y1, Y2} | 0.29, 0.5, 150, 425 | UI mV | Hit Ratio = 5×10-5 |
Notes:
1. Power-on Initialization Time is the time from when the power supply voltages reach and remain above the minimum recommended operating supply voltages to the time when the module is fully functional.
2. The single ended input voltage tolerance is the allowable range of the instantaneous input signals.
Optical Characteristics
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Typical | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Wavelength Assignment | L0 | 1264.5 | 1271 | 1277.5 | nm | |
| L1 | 1284.5 | 1291 | 1297.5 | nm | ||
| L2 | 1304.5 | 1311 | 1317.5 | nm | ||
| L3 | 1324.5 | 1331 | 1337.5 | nm | ||
| Transmitter | ||||||
| Side Mode Suppression Ratio | SMSR | 30 | dB | |||
| Total Average Launch Power | PT | 8.3 | dBm | |||
| Average Launch Power, each Lane | PAVG | -4 | 2.3 | dBm | ||
| Optical Modulation Amplitude (OMA), each Lane | POMA | -4 | 3.5 | dBm | 1 | |
| Difference in Launch Power between any Two Lanes (OMA) | Ptx,diff | 6.5 | dB | |||
| Launch Power in OMA minus Transmitter and Dispersion Penalty (TDP), each Lane | -4.8 | dBm | ||||
| TDP, each Lane | TDP | 2.6 | dB | |||
| Extinction Ratio | ER | 3.5 | dB | |||
| Relative Intensity Noise | RIN | -128 | dB/Hz | 12dB reflection | ||
| Optical Return Loss Tolerance | TOL | 20 | dB | |||
| Transmitter Reflectance | RT | -12 | dB | |||
| Transmitter Eye Mask Definition {X1, X2, X3, Y1, Y2, Y3} | {0.25, 0.4, 0.45, 0.25, 0.28, 0.4} | |||||
| Average Launch Power OFF Transmitter, each Lane | Poff | -30 | dBm | |||
| Receiver | ||||||
| Damage Threshold, each Lane | THd | 3.3 | dBm | 2 | ||
| Total Average Receive Power | 8.3 | dBm | ||||
| Average Receive Power, each Lane | -13.7 | 2.3 | dBm | |||
| Receiver Reflectance | RR | -26 | dB | |||
| Receiver Sensitivity (OMA), each Lane | SEN | -11.5 | dBm | |||
| Stressed Receiver Sensitivity (OMA), each Lane | -9.6 | dBm | 3 | |||
| Difference in Receive Power between any Two Lanes (OMA) | Prx,diff | 7.5 | dB | |||
| LOS Assert | LOSA | -28 | dBm | |||
| LOS Deassert | LOSD | -15 | dBm | |||
| LOS Hysteresis | LOSH | 0.5 | dB | |||
| Receiver Electrical 3 dB upper Cutoff Frequency, each Lane | FC | 12.3 | GHz | |||
| Conditions of Stress Receiver Sensitivity Test (Note 5) | ||||||
| Vertical Eye Closure Penalty, each Lane | 1.9 | dB | ||||
| Stressed Eye J2 Jitter, each Lane | 0.3 | UI | ||||
| Stressed Eye J9 Jitter, each Lane | 0.47 | UI |
Notes:
- Even if the TDP < 0.8 dB, the OMA min must exceed the minimum value specified here.
- The receiver shall be able to tolerate, without damage, continuous exposure to a modulated optical input signal having this power level on one lane. The receiver does not have to operate correctly at this input power.
- Measured with conformance test signal at receiver input for BER = 1×10-12.
- MVertical eye closure penalty and stressed eye jitter are test conditions for measuring stressed receiver sensitivity. They are not characteristics of the receiver.
Digital Diagnostic Functions
The following digital diagnostic characteristics are defined over the normal operating conditions unless otherwise specified.
| Parameter | Symbol | Min | Max | Unit | Notes |
| Temperature monitor absolute error | DMI_Temp | -3 | +3 | ℃ | Over operating temperature range |
| Supply voltage monitor absolute error | DMI_VCC | -0.1 | +0.1 | V | Over full operating range |
| Channel RX power monitor absolute error | DMI_RX_Ch | -2 | +2 | dB | 1 |
| Channel Bias current monitor | DMI_Ibias_Ch | -10% | +10% | mA | |
| Channel TX power monitor absolute error | DMI_TX_Ch | -2 | +2 | dB | 1 |
Notes: 1. Due to measurement accuracy of different single mode fibers, there could be an additional +/-1 dB fluctuation, or a +/- 3 dB total accuracy.
What is an (Fiber) Optical Transceiver?
An Optical transceiver module is the core part of optical communication devices. It uses fiber optical technology to send and receive data through completing the process of optical signal – electrical signal / electrical signal – optical signal conversion. An optical transceiver module consists of two parts: the receiving part and the transmitting part. The receiving part realizes the photo-electric conversion, and the transmitting part realizes the electro-optical conversion.
Usually, one end of the transceiver will be connected to a cable and the opposite end of will have a special connector for fitting it into specific models of enterprise-grade Ethernet switches, routers or network interface cards
How to Classify Optical Transceivers?
In order to meet a variety of needs of transmission, the manufacturers launched a variety of categories of optical modules. Below are some common methods to classify them.
1)Sort by Rate
400GE optical transceiver module,
200GE optical transceiver module,
100GE optical transceiver module,
40GE optical transceiver module,
25GE optical transceiver module,
10GE optical transceiver module and etc.
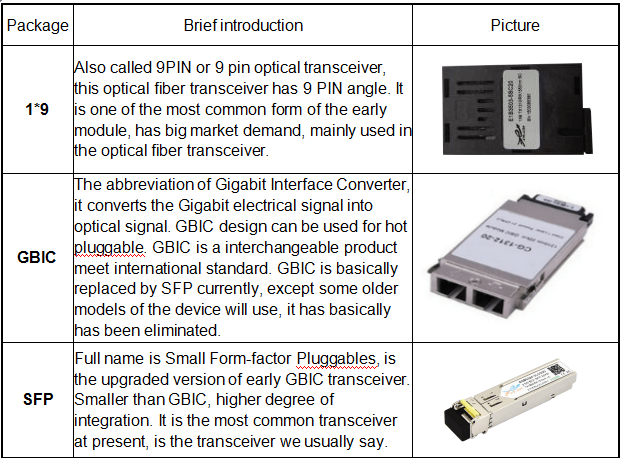
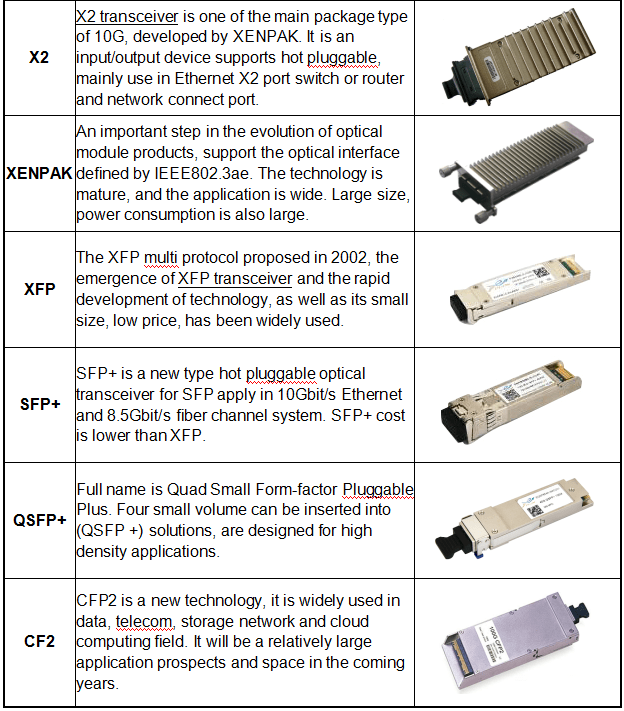
2)Sort by Package
The higher the transmission rate of the optical transceiver, the more complex the structure. In order to meet the needs of different structures, a variety of packaging types of optical transceiver modules were designed. For example, XFP, SFP, SFP+ for 10G transceivers, QSFP+ for 40G transceivers, CFP4, CFP2 and QSFP28 for 100G transceivers, as well as the latest OSFP and QSFP-DD for 400G transceivers.
- XFP (10GB Small Form-factor Pluggable) optical module: “X” is the abbreviation of Roman numerals 10, all XFP modules are 10G optical module. The XFP optical module supports LC fiber optic connectors and supports hot plugging. Compared to SFP+ and SFP optical modules, XFP optical modules are larger and longer.
- SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) optical module: smaller than XFP, SFP optical modules support LC fiber optic connectors, hot plugging.
- SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) optical module: SFP+ refers to the increased rate of SFP module, sensitive to EMI.
- QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) optical module: four-channel small hot plugging optical module. The QSFP + optical module supports MPO fiber connectors, which are larger in size than SFP + optical modules.
- CFP (Centum Form-factor Pluggable) optical module: length × width × height of CFP is defined as 144.75mm × 82mm × 13.6mm, high-speed, hot plugging and supporting for data communications and telecommunications applications.
- QSFP28 optical module: the interface package size of QSFP28 is the same with QSFP+, which is mainly used in Data Center application.
- OSFP (Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable) optical module: the OSFP is a new pluggable form factor with eight high speed electrical lanes that will initially support 400 Gbps (8x50G). It is slightly wider and deeper than the QSFP but it still supports 32 OSFP ports per 1U front panel, enabling 12.8 Tbps per 1U.
- QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density) optical module: QSFP-DD is a new module and cage/connector system similar to current QSFP, but with an additional row of contacts providing for an eight lane electrical interface. It is being developed by the QSFP-DD MSA as a key part of the industry’s effort to enable high-speed solutions.
3)Sort by Physical Layer Standard
In order to allow the data to be transmitted in different conditions and applications, optical communication industry defined of a variety of different physical layer standards, which resulting in a variety of optical transceiver modules supporting different standards.
For example, IEEE and MSA industry alliances have set several criteria for the 100G QSFP28 optical modules, like SR4, LR4, ER4, PSM4, CWDM4 and etc.
4)Sort by Pattern
As we all know, fiber can be divided into single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber. In order to use different type of fiber, we also classify optical transceiver modules into single-mode optical modules and multi-mode optical modules.
Single-mode optical module is used to match single-mode fiber with better transmission capacity, which is suitable for long-distance transmission.
Multi-mode optical module is used to match multi-mode fiber. Multimode fiber has the defect of mode dispersion, its transmission performance is poorer than single-mode fiber. However, with better cost performance, they are popular in smaller capacity, short distance transmission.
How to choose the right optical module?
With the rapid development of information technology, the application of optical communication has become more and more popular. With the advantages of large capacity and high-speed transmission, Fiber Optic Transceiver Modules is playing a more and more important role. Where there is fiber, the optical module is needed, and the selection and purchase of the optical module has become the focus of the front-line engineering technicians or purchasing personnel.
There are many types of optical transceivers on the market, often dazzling. So, how to choose the most suitable module in many different speed, different packaging, different functions of the Optical Transceiver Module? We will give you some tips.
Choose the module based on your usage environment
How fast the speed of transmission you need? 155M, 1G, 10G or 100G? The higher transmission rate means higher cost investment. For example, the application environment of FTTH, it’s enough to use about 1G speed products for current bandwidth. It’s not necessary to choose 10G products with more money.
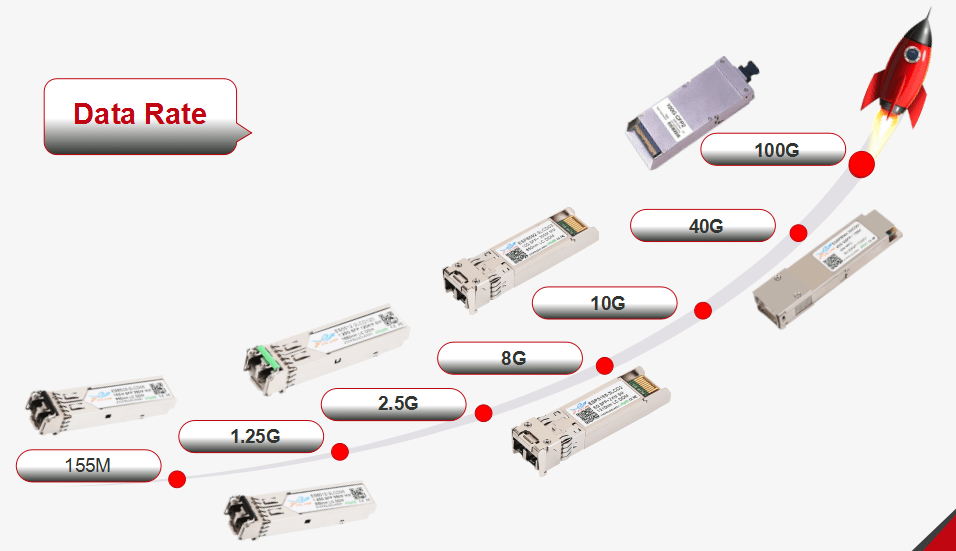
Optical Transceiver Module Data Rate
Transmission distance
The common optical modules are divided into short distance (300M-2KM), middle distance (10KM-40KM), long distance (>40km), The farther the transmission distance, the higher the technical and technological requirements of the optical module.
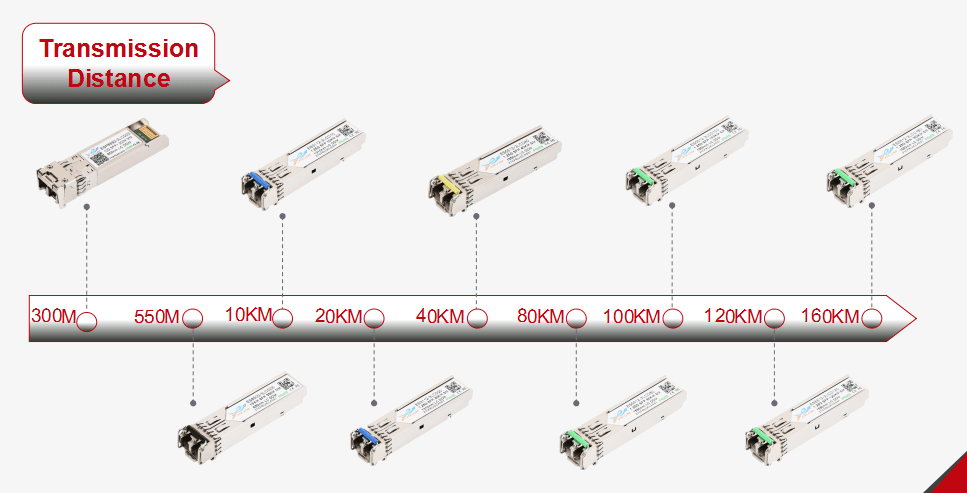
Optical Transceiver Module Transmission Distance
Modules Compatibility

Modules Compatibility
When purchasing optical modules, need to confirm whether it can be compatible with your devices. Common switch brands like CISCO, HUAWEI, H3C, Juniper, D-link, HP, IBM, dell, Mikrotik etc., modules need to be tested compatibility before shipment. Before purchasing, it is best to confirm that it can be perfectly compatible with the corresponding brand switch.
Select the original one or compatible one according to the budget situation
The original module is reliable but the price is too high, compatible module is cost-effective, comparable to the original module. Different users need to make specific choices according to the budget.
After-sale service
QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km Optical Transceiver
| Brand |
OEM |
|---|---|
| Model |
QSFP+ 40G LR4 1310nm 10km |




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.