DSL vs Ethernet vs Fiber
What Is DSL?
DSL is short for Digital Subscriber Line. It is one of the oldest Internet technologies which is used by homes or businesses to send and receive data via copper telephone lines. It seems much like dial-up because they both use your phone line to transfer data and connect you to the internet. However, DSL is a step above dial-up internet: It enables you to make a phone call and go on the internet at the same time while you can only do one at a time when using dial-up connections. There are two types of DSL: Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) and Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL). SDSL offers equal upload and download speeds while ADSL offers download speeds higher than upload speeds.
What Is Ethernet Cable?
Ethernet cables are the most common network cable type in our daily life. It connects network devices such as PCs, routers, and switches within a local area network. The commonly used Ethernet cord types are Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7 and the new category Cat8. Each new promotion of category supports increasingly faster bandwidth speeds and improves upon the signal-to-noise ratio. Among these Ethernet cables, Cat6 cables remain popular in home use, and Cat7 and Cat8 cables are aimed at business users who need higher speeds and higher bandwidth.
What Is Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cables are a relatively new method for internet access at home and business. When it comes to fiber optic cables, fast speed is what people often evaluate. Indeed, optical fiber cables used for the Internet are synonymous with high speed, especially when using over long distances. How does fiber optic cable work? The fiber cable contains strands of glass or plastic fibers inside an insulated casing. With this method, the strands of fibers can carry data through light inside the line. There are two main types of fiber optic cables: Single Mode Fiber (SMF) and Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF).
Difference in DSL vs Ethernet vs Fiber Cable
To make better decisions on DSL, Ethernet cables, and fiber optic cables, the following elements on which they are different need to be considered.
Structure
To some extent, DSL cables have the similar structure as Ethernet cables: both of them are constructed of copper cables to transfer data using electrical impulse. The difference is that DSL uses the standard phone plug while typical Ethernet cables have two extra pairs of twisted copper wires with a larger plug as shown in figure below. As for the fiber optic cable, the structure is evidently distinct. It delivers data using fiber instead.
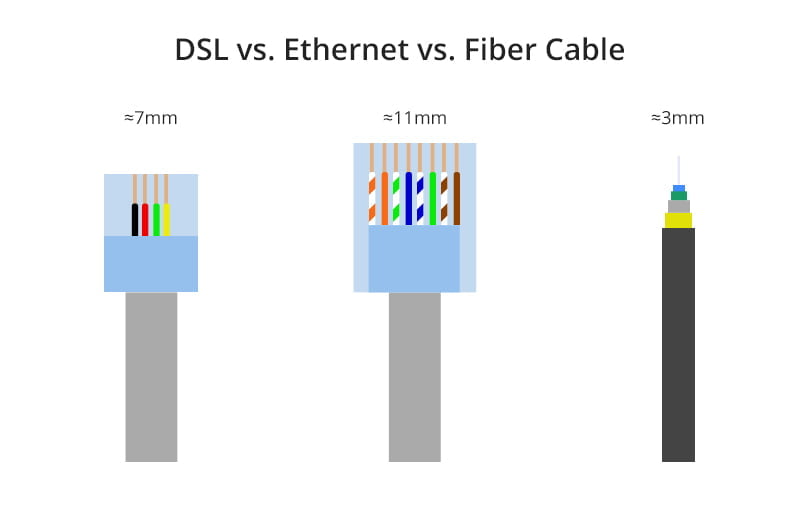 Figure: DSL vs Ethernet cable vs fiber cable
Figure: DSL vs Ethernet cable vs fiber cable
Speed
Speed is a key point for choosing the best cable for the Internet. Historically, DSL speeds are slow and it is difficult to specify the exact speed. How fast the DSL is often depends on your DSL internet provider and the technology used, generally less than 1 Mbps, but still some up to 100 Mbps.
Ethernet speed has been limited to 10 Mbps once a while, however, the development of Fast Gigabit offers rates of up to 100 Mbps and now Gigabit Ethernet is getting popular, delivering data at a higher rate. For home use, in general, Ethernet cable download speed usually starts from 10Mbps to 500Mbps, and the upload speed is from 5Mbps to 50Mbps.
Fiber optic cable speed is the fastest among these three internet access technologies. The download and upload speed of a fiber patch cord can be anywhere from 250Mbps to 1000Mbps and not affected by the distance from ISP. Fiber optic cables usually contain many strands, and a single strand of fiber optic cable has been proven to be able to carry data at up to an extremely fast 100Tbps, which suggests the superior speed of fiber optic cables.
Security
DSL provides customers with a dedicated line, therefore it is less likely to cause Internet security issues. The information passes between the central office and the customers’ home without passing through connection to other customers’ modem. Ethernet cables using electrical signals are vulnerable to electromagnetic interference and easy to get intercepted by hackers at the hardware level. The light transmission in fiber optic cables is not susceptible to EMI and RFI as the copper connections do and any physical break in the system is easy to identify, thus there is no way for hackers to listen in on the transmission. Overall, fiber optic cables are the most secure one with a low security and privacy risk.
Cost
The cost of DSL, Ethernet or fiber cable varies depending on your specific need, your location, your provider, the terms of the agreement and other elements. When you are about to install one of them for internet access, you should take not only the cable cost into account but also the installation and activation fees. Typically, the fiber optic internet cost is the most expensive one because the fiber installation is more complicated than coax with many variables to be considered and you need to pay for the devices matched with fiber optic cables, professional installers, etc. Since the Ethernet cable infrastructure is more expensive than the telephone, ethernet cable installation costs more compared with DSL.
Based on the elements above, you may find that DSL, Ethernet cables, and fiber optic cables all have their own benefits and shortages.
| Speed | Security | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSL | Low | Higher | Low |
| Ethernet cable | Faster | Low | Higher |
| Fiber optic cable | Fastest | Highest | Highest |
For those businesses that need the fastest internet connections and highest security, there is no doubt that fiber optic cables will become the best choice. For those who care about the whole budget, DSL and Ethernet cables are both applicable.
Conclusion
Overall, though fiber optic cables have not been so available as the scale of DSL and Ethernet cables, the big advantages of fast speed and high security, which is also the tendency of the network, can not be denied. We can expect that fiber optic cables will develop to a point that it will become the mainstream of internet connections.
