Fiber patch cords and fiber pigtails are two kinds of commonly used network connectivity components in fiber optic network. They share many common characteristics, and in some ways there are also some differences. To understand the similarities and differences will help you make the best choice for your application. This post will give you a better understanding of the differences between fiber optic pigtails and patch cords.Fiber Patch Cord
A patch cord is a length of cable with connectors on each end that is used to connect end devices to power sources. Patch cords are made from either single or multi-fiber cables and connected at each end with fiber cable connectors. Sometimes fiber patch cables are called jumpers, especially if they are simplex or duplex. The connectors are selected to mate with the interfacing equipment or cable connectors. The fiber can be either tight or loose buffered and can be made of various diameters (1.2 mm to 3.0 mm are common).
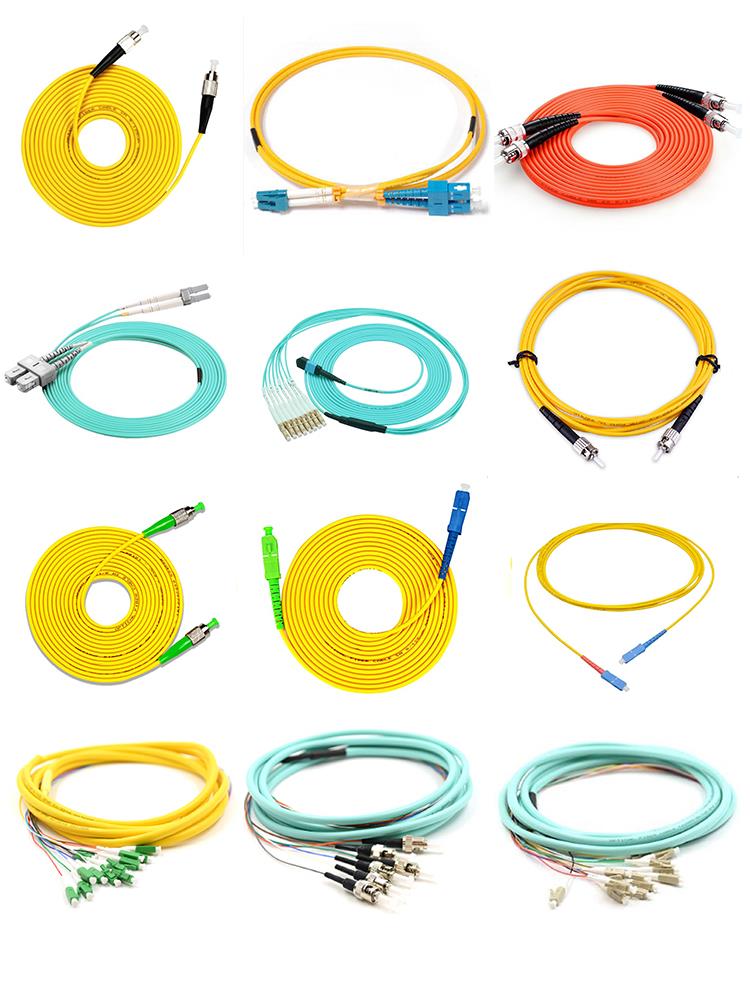

Fiber Pigtails
Pigtails bridge a critical junction in the fiber-optic network. The fiber pigtail is a fiber cable with a factory installed connector on one end and an unterminated fiber on the other, so that the connector side can be linked to the equipment and the other side can be melted with optical cable fibers or stripped and fusion spliced to a single fiber of a multi-fiber trunk.
Structural Difference Between Fiber Patch Cords and Fiber Pigtails
Fiber optic patch cables and fiber optic pigtails structurally have much in common. They are both available in single mode and multi-mode, and they can be made into simplex and duplex. Besides, both fiber patch cords and pigtails can terminate with many kinds of fiber optic connectors, including FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, MPO, MU, SMA, FDDI, E2000, DIN4, and D4.

The major physical difference between fiber patch cord and pigtail is that fiber patch cord is a fixed length piece of cable with fiber connectors on each end while fiber pigtail has fiber connectors on only one end of the cable. Fiber optic patch cords can be cut into shorter lengths to make two pigtails.Applications of Fiber Patch Cords and Fiber Pigtails
Fiber optic patch cords and pigtail fibers provide interconnect and cross-connect of applications over installations in entrance facilities, telecommunications rooms, and data centers. They are available in OM4, OM3, OM2, OM1, or OS1/OS2 fiber types, and can meet the demands of Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gigabit Ethernet and high speed Fibre Channel. However, they have their respective application areas, too.
Fiber patch cords are commonly used to connect ports on fiber distribution frames (FDFs). They support network applications in main, horizontal and equipment distribution areas and are available in optical fiber riser cable (OFNR), and low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) rated jacket materials to comply with local cabling ordinances. They also support high speed (10/40 Gbs) telecommunications. Fiber optic patch cords can also be used in many areas, such as integrated optics, laser detection and display, and materials processing, etc.
Fiber optic pigtails support fusion splice field termination applications. They should be installed in the protected and splice needed place, so they are usually used with optical fiber management devices like optical distribution frame (ODF), splice closures and optical fiber distribution boxes. Applications of fiber pigtails are found everywhere, but most commonly in optical assemblages or optical components. For example, there are waterproof fiber optic pigtails with thick polyethylene (PE) jacket and large diameter used for outdoor applications.Conclusion
Although patch cords and fiber pigtails look very similar, they still have some differences in structure and application. A better understanding of the differences can help you choose the right one in your application.
